How Blended Water Supplies Impact Water Treatment
Where does my water come from?
The source(s) of water supplied to cooling towers, boilers, and processes may vary greatly daily or even hourly. The impact this has on water systems must be closely monitored to avoid scale, deposits, corrosion, inefficient water usage, and other negative impacts on operational costs.
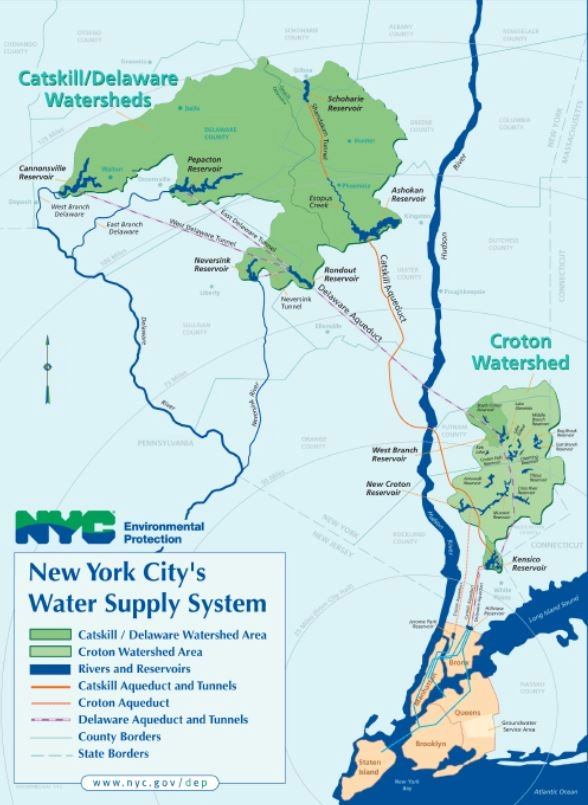
The New York City water supply is a good example, providing over 1.2 billion gallons/day of domestic water to more than 8 million NYC residents, 1 million users from 4 upstate counties, and the city’s many visitors. The water system is made up of aqueducts, distribution pipes, reservoirs, and water tunnels offering a total system storage capacity of close to 550 billion gallons. There are three separate systems that bring water from upstate to the city to fit this need; the Croton, to the east of the Hudson River, and the Catskill and Delaware on the west.
What is in my water?
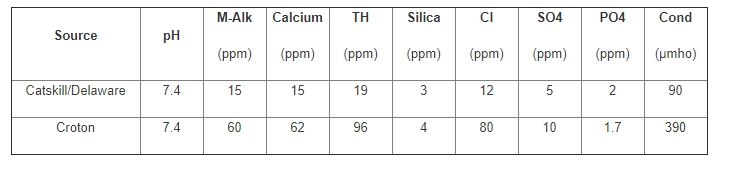
Since the opening of the Croton Water Filtration facility in May of 2015 water treatment professionals across the five boroughs have faced issues with a blended water supply. The neighborhoods of New York City often receive a combination of all three water supplies, the Croton, Catskill, and Delaware. Operational decisions about the City’s water supply, including the proportion of water from each of the systems, are often made on an hourly basis, creating a constantly changing chemistry of a building’s incoming water. There is currently no formal notification system in place as to when a change in water supply might occur or what the blend could consist of. When Croton water is introduced to the system there could be areas within the same borough that are 100% Croton water or 100% Catskill/Delaware water, and others that are blended at varying percentages. Conductivity measurements are relied upon to gain an understanding of what water source you’re dealing with at each location throughout the city. In general, the conductivity of the Catskill/Delaware supply is in the 90-100 µmho range while the conductivity of the Croton water is consistently in the 350-500 µmho range. For many facilities, when the make-up water has a conductivity greater than 100, it is assumed some level of blending is taking place. The chart below details some key differences in the inorganic chemistry of the water supplies:
 How does this affect my water treatment?
How does this affect my water treatment?
From a water treatment perspective, fluctuating supply/makeup water sources present significant issues for system control. To understand this concept, it’s important to understand cycles of concentration (COC). Cooling tower cycles are typically controlled by the conductivity of the water in the system. When the conductivity reaches a predetermined set point, the controller bleeds water from the system and replaces it with fresh makeup water. The makeup water has a lower concentration of salts and dilutes the system water. With consistent makeup water, this control method is simple and quite effective because water treatment professionals can predict the levels of dissolved solids in the system water (important for inhibitor choice), determine hold times (the length of time the water stays in the system), and estimate water use.

Cooling tower treatment, for example, commonly bases the cycles of concentration calculation upon conductivity readings. The incoming city water conductivity is multiplied by the targeted number of cycles to use as the conductivity set point. Over-cycling could lead to issues with scale deposition when the concentration of dissolved solids gets above the saturation point. Under-cycling can lead to unnecessary water use, lower operational efficiency, and depending on control method, inaccurate inhibitor residuals. A constantly changing water supply makes it almost impossible to consistently maintain the targeted cycles for a specific system. This is particularly true when there is no way of knowing what type of water you could be receiving at a facility at any given time. Changing the chemistry of the makeup water also changes the target cycles. A varying water supply requires consistent on-site testing of the makeup water and an experienced water treatment professional to effectively manage the fluctuating conditions.
Chem-Aqua has the perfect blend of expertise and experience to manage your changing water demands. Contact a local representative today to review your water treatment program.