The Possible Achilles’ Heel of EVs and Energy Storage
Takeaways
- Battery technology is progressing slowly and advances in lithium-metal are not yet commercially available
- Federal EV battery incentives pertain to countries with US free trade agreements: Australia, Canada, and Chile
- Battery supply is constrained by metal mining and production is limited by complex and costly process technologies
- More research and product production methods are imminently needed
The Possible Achilles’ Heel of EVs and Energy Storage
Battery production for electric vehicles should be a concern. For one, the US has neither the resources nor the production capacity to meet the demand of EV manufacturers. Second, as a national security concern, not having the requisite production infrastructure to support energy transformation leaves the US vulnerable to economic decline and energy price increases. Third, to navigate energy transformation it’s imperative to establish battery production for grid stability and resiliency, particularly when introducing renewable energies.
Currently, lithium-ion batteries are the core foundation for EVs and most vehicle manufacturers are planning to transition to all elective vehicles in the near future. California might ban the sale of new cars running only on gasoline by 2035. The issue is the production of EVs is inextricably linked to the availability of batteries that are limited by supply constraints in both battery metals and production capacity. Our focus is on battery supply chains and production.
Battery Supply Chains
The big issue around EV batteries is assuring an adequate supply of materials at a reasonable price. To better understand the EV supply chain let’s look at the common raw materials namely metals and their associated costs. The four primary metals in a lithium-ion battery commonly used in most EVs are lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese. EV batteries use nickel-manganese-cobalt cathodes, with 60% nickel and 20% of cobalt and manganese.
By reviewing some of the metal supply data from the US Geological Survey and pricing data we can achieve better insight into EV battery supply chains. Some of these materials are relatively abundant like manganese and nickel while others like lithium and cobalt are limited. Lithium and cobalt are concentrated in a handful of countries. A limited supply of cobalt leads to high prices as well as efforts to reduce cobalt in battery production.
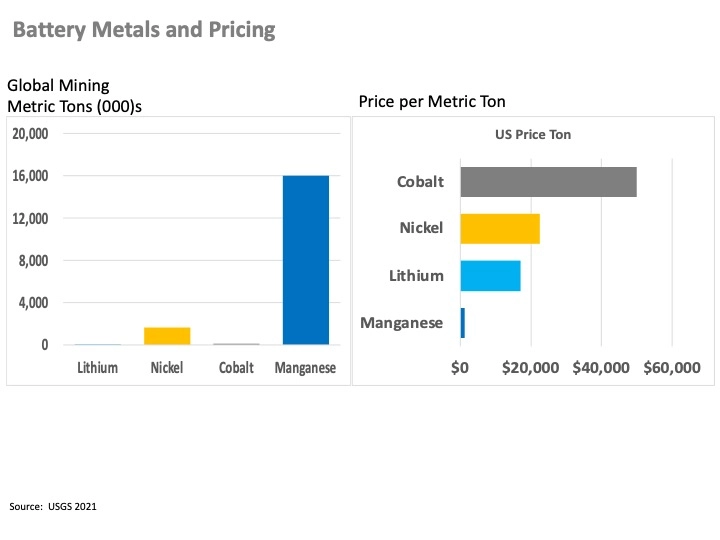
The main issue is the availability of metals used in battery production. Material demand should correspond respectively to its battery composition proportion with the exception of cobalt as solid and dry battery processing expand. To take advantage of the recent incentives introduced in the Inflation Reduction Act, materials must originate from countries that have Free Trade Agreements with the US. Countries with metals resources of lithium, nickel, cobalt, or manganese with a free trade agreement with the US include Australia, Canada, and Chile.
Battery Production Technology and Economics
A key energy storage performance metric is watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg) which is essentially the duration of power relative to battery weight. The focus is to increase battery power and longevity while reducing its weight. Advances in reducing cobalt and battery weight are within reach but not yet commercially available.
The focus currently is on improving production efficiencies with existing technologies and production methods that are extremely capital intensive. Tesla has shifted towards dry electrode processing in its larger 4680 battery cells to increase capacity and reduce production costs. Dry electrode processing reduces chemical slurry preparation costs by reducing production time, reducing energy consumption, and lowering volatile fume emissions in solvent recovery.
The problem is that the US does not have the production capacity or metal resources.
Battery Production
Lithium-ion battery production is capital intensive, expensive, and time-consuming. The battery production process comprises over a dozen distinct complex processes from electrolyte preparation and cell assembly to electrochemistry activation and quality control.
While China is not a leader in metal mining, they are the leading supplier of EV batteries as well as in the processing of lithium, cobalt, manganese, and nickel. To scale EV market growth batteries are crucial. The US is constrained without access to metals and processing capabilities to build batteries. The bottom line is that the US needs to invest not only in the grid infrastructure to support EV charging but also in battery production to sustain EV market growth.
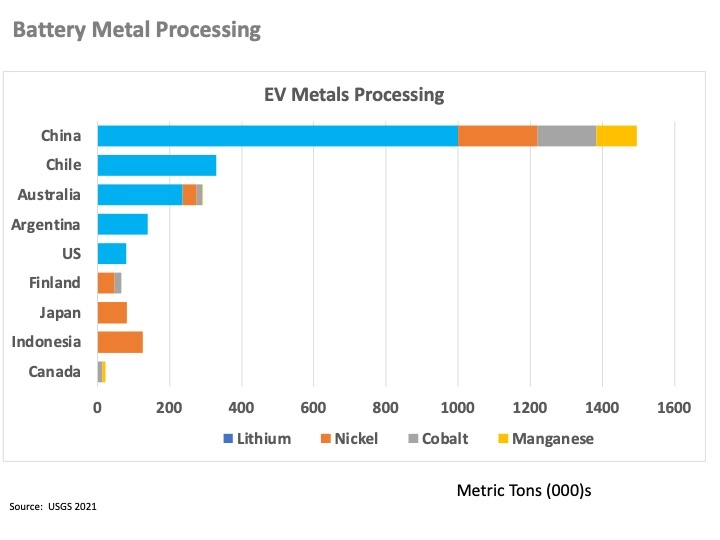
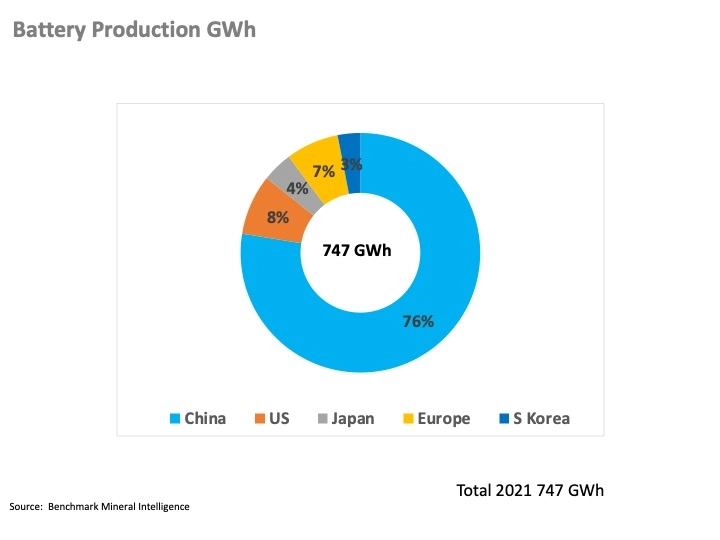
Tesla indicates that its demand for lithium-ion batteries will increase from approximately 250 GWh in 2021 to 2 TWh by 2030. Global battery production in 2021 was 747 GWh and according to Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, China is the leading producer of battery metals and lithium-ion battery production. The top battery manufacturing companies in China are Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL), and BYD. The call to action is coordination between academia, R&D, and the VC community to identify feasible and viable new technologies and production methods.
Action Plans
- The greatest challenge for EV manufacturers is battery technologies and robust supply chains
- Battery process technologies are complex and costly so input from chemistry, engineering, and production is monumental
- Coordination between academia, R&D, and the VC community to ferret out feasible and viable new technologies
Michael S Davies, CFA, CMVP
Founder
Green Econometrics
Linkedin: Michael S Davies, CFA – Founder, Data Scientist – Green Econometrics/








