Bit Depth And Why It Matters
Despite a good deal of confusion – and unfortunately, misrepresentation – in the digital signage industry, bit depth is actually an important metric for purchasers, advertisers and content creators to consider.
Bit depth, sometimes referred to as color depth or color capacity, can be a very technical, in-the-weeds concept, but here we’ll keep it fairly simple and describe the basics, so you can better understand this term which is found on virtually all digital signage cut sheets.
Bits Are Binary Values
A bit refers to a binary value (0 or 1), or simply off or on. For example, a normal light switch is binary, but a dimmable light switch has multiple levels.
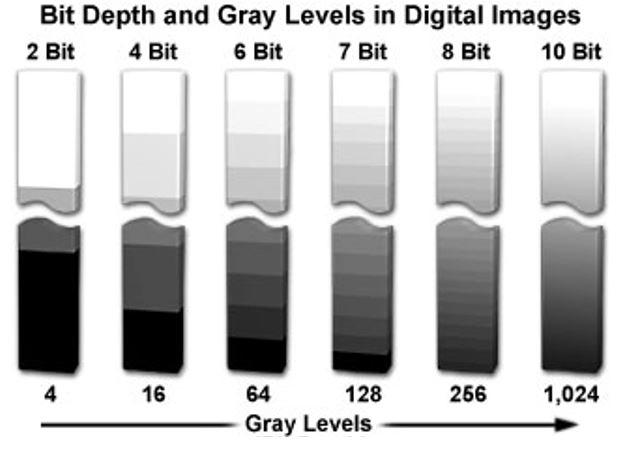
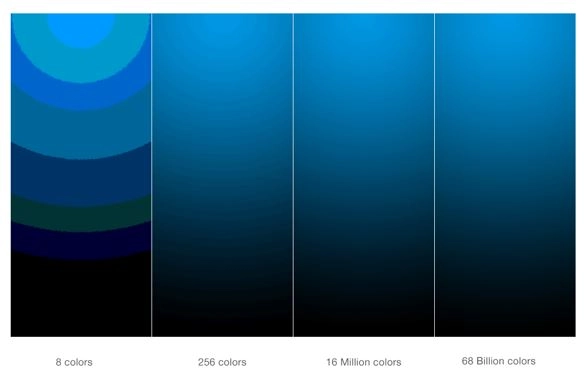
For imagery, one bit is black and white (no shades of gray). Two-bit expands to four total levels (white, black, white-gray, and black-gray). Each additional bit doubles the number of levels from before. Two more bits, for example, quadruples the number of color levels. Refer to the Bit Color Chart in Figure 1 to see how color levels exponentially increase with added bits.
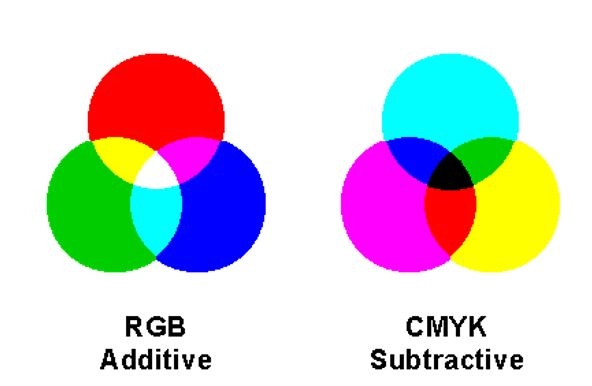
Additive Color vs Subtractive Color
Additive color (used in displays) is different than subtractive color (used in printing). If you’ve ever bought ink cartridges for your printer, you will be familiar with the CMYK colors – cyan, magenta, yellow and key (black). These are the literal opposites of RGB colors – red, green and blue.
In additive color, red and blue make magenta. Blue and green make cyan. Green and red make yellow. Equal parts RGB make white. Subtractive color flips this, as magenta and yellow make red, cyan and yellow make green, and magenta and cyan make blue. Equal parts CMY makes black. This might not be intuitive, but it is absolutely true. Consider this: when a display is showing RGB as 255/255/255, it shows white. When the display is off, it’s black. If you’re printing, the paper alone is white and putting equal parts CMY on the same spot will make it black, in theory. In reality, it’s brownish due to pigment quality.
But what do these color calculations have to do with bit depth and digital displays, you ask?
Bit Depth and LED Displays
An LED display is generally built with red, green, and blue LEDs. If you control each of these color channels separately, a wide spectrum of colors is available.
But what if each channel had only one bit of control, on or off? Simply put, this wouldn’t be very effective. It would allow for just eight colors (red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, yellow, white, and black) for each pixel. As you can imagine, this would be a very rudimentary display. The good news is that except for some extremely basic informational signage, virtually all digital signage today outperforms these basic color levels.
If each channel has two bits of control (6 total bits for the RGB pixel), then the color palette increases from 8 colors to 64 colors (4 x 4 x 4). Four bits each (12 total) yields 4,096 colors.
 Is More Better?
Is More Better?
By logical extension, more bits would be better, right? Yes, but only to a point. Many LED displays are eight-bit per channel (24-bit total), which generates about 16.7 million total colors (256 x 256 x 256).
However, the typical human eye can discern about 7 to 10 million shades of color. Thus, more than 16 million should be plenty. This is why 24-bit color is the standard for LED displays, TVs, computers and a host of other displays.
 Other Callouts and Data Charts to Include
Other Callouts and Data Charts to Include
 Figure 1 – Bit Color Chart
Figure 1 – Bit Color Chart
1-bit color 21 = 2 colors (often black and white)
2-bit color 22 = 4 colors
3-bit color 23 = 8 colors
4-bit color 24 = 16 colors
5-bit color 25 = 32 colors
6-bit color 26 = 64 colors
8-bit color 28 = 256 colors
12-bit color 212 = 4,096 colors
14-bit color 214 = 16,384 colors
16-bit color 216 = 65,536 colors
Read more at snadisplays.com