As Export Values Rise, American Farmers Face a Trade Crisis
Key Points:
- U.S. agricultural exports are being hampered by transportation issues, leading to a loss in sales potentially as high as 22%.
- In 2021 from January through July, the dairy industry was forced to spend almost a $1 billion in additional costs to make up for supply chain problems.
- American farmers who are experiencing losses due to inconsistent exportation can regain losses by selling goods in the domestic market.
Commentary:
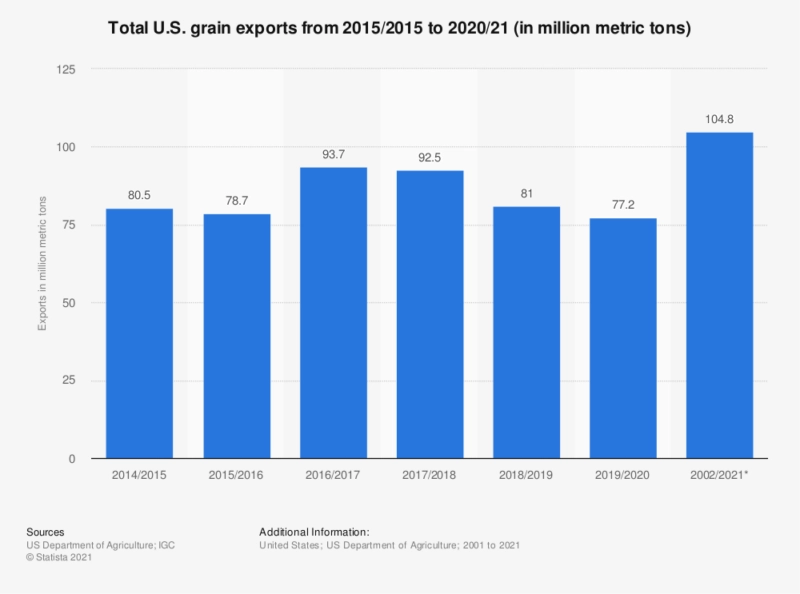
The impact of the last year of supply chain disruptions stretches to almost every industry, and this includes the American farming industry. U.S. farmers’ exports are being severely impacted as shippers pass on U.S. exports in favor of stocking on goods from Asia and running Asia-to-U.S. trade routes. According to the International Grains Council, the U.S. shipped 77.2 million metric tons in just grain alone between 2019 and 2020, playing just one piece of the U.S.’ exports puzzle.
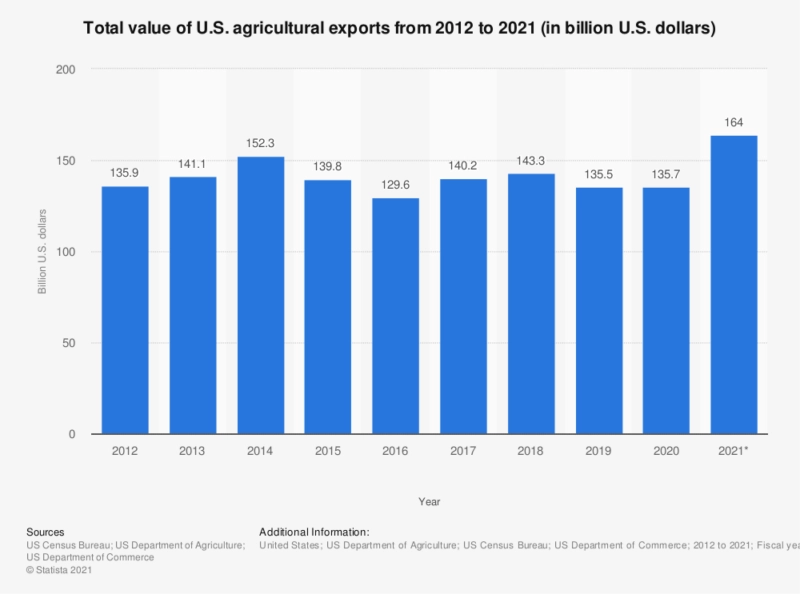
The Office of the United States Trade Representative reports U.S. farmers export more than 20 percent of what they produce; with so many investments in exports across the entire farming industry, losing out on these exports can be costly. Shawna Morris, Senior Vice President of Trade Policy at the U.S. Dairy Export Council, explained that the dairy industry has lost billions of dollars due to added costs they have had to endure to deal with these issues.
“It’s been a tremendous barriers for the companies actually working to move product overseas, whether that’s milk powder, cheese, or other dairy ingredients, and ultimately that flows back to the farmer level by eroding the markets that our exports have worked so har dot build as additional outlets for American-made milk,” Morris said.
It doesn’t just stop with the dairy farmer, either. While dairy exports account for 15% of the markets total production, the soybean industry has an even bigger percentage of exports; the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service reported in 2018 that exports accounted for 50% of soybean crop production. Jim Sutter, CEO of the U.S. Soybean Export Council and chair of the U.S. Agricultural Export Development Council, puts that number even higher, claiming 60% of the current soybean crop is exported.
“The majority [of our commodities] is shipped in bulk ocean-going vessels. Freight rates have more than doubled this year for ocean freight, but just in the last two weeks they’ve come back down by about 25% or 30%. It’s been extremely volatile lately, and I think what it shows is people need to keep watching this and it will change very quickly,” Sutter said.
Both Sutter and Sam Eder, CEO of supplier management company Big Wheelbarrow, say that American farmers need to think outside the box to find new solutions that can fix these problems. One of those solutions, according to Eder, is to sell products in the United States rather than waiting to ship these products overseas.
“For American farmers that are looking to get into the retail market, we give you two pieces of advice. First, sell direct to retailers when possible,” Eder said. “Selling directly to a retailer either through their warehouse or direct to a store gives them a win-win. Farmers get the best possible price for their goods, and retailers get the best possible margin.”
“The second way is to find a wholesaler who can repack goods for the retail market. Obviously, it’s not as lucrative a sale as going direct, but it saves the farm from any major capital outlay to get into that supply chain,” Eder said.








